
The degree measure of a minor arc or semicircle AB of circle O is the measure of its central angle AOB. Ray VR is the bisector of angle PVQ if and only if ray VR (except for point V) is in the interior of angle PVQ and mPVR = mRVQ.
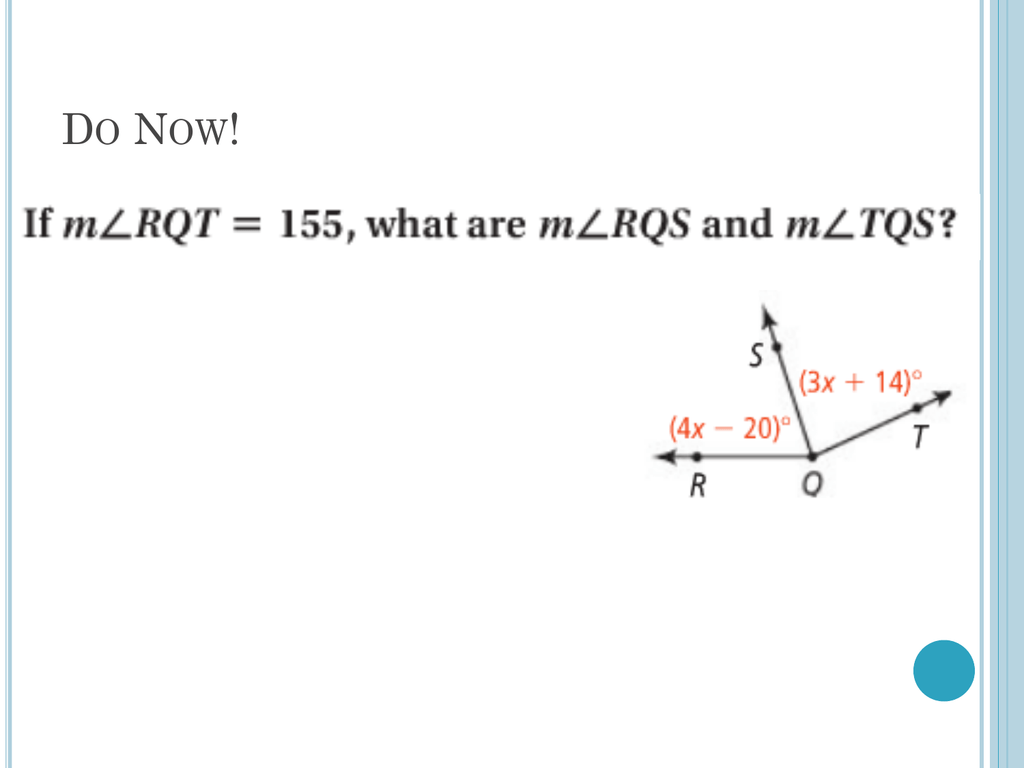
If ray VC (except for point V) is in the interior of angle AVB, then mAVC + mCVB = mAVB. If rays VA and VB are opposite, then mAVB = 180.Īngle Measure Postulate: Angle Addition Property If rays VA and VB are the same, then mAVB = 0.Īngle Measure Postulate: Straight Angle Assumption Given any ray VA and any real number r between 0 and 180, there is a unique angle BVA in each half-plane of VA such that mBVA = r.Īngle Measure Postulate: Zero Angle Assumption The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.Īn angle is the union of two rays that have the same endpoint.Īngle Measure Postulate: Unique Measure AssumptionĮvery angle has a unique measure from 0 to 180.Īngle Measure Postulate: Unique Angle Assumption The intersection of two sets A and B is the set of elements which are in both A and B. The union of two sets A and B is the set of elements which are in A, in B, or in both. If B is on segment AC, then AB + BC = AC. If two points on a line have coordinates x and y, the distance between them is |x - y|. On a line, there is a unique distance between two points. Rays AB and AC are opposite rays if and only if A is between B and C. The ray with endpoint A and containing point B consists of the points on AB and all points for which B is between it and A. The segment with endpoints A and B is the set of points A and B and all points between A and B. Two coplanar lines m and n are parallel, written m || n, if and only if they have no points in common or they are identical. Two different lines intersect in at most one point. (2) Given a plane in space, there is a point that is not in the plane. (1) Given a line in a plane, there is a point that is not on the line. Point-Line-Plane Postulate: Dimension Assumption Point-Line-Plane Postulate: Number Line AssumptionĮvery line is a set of points that can be put into a one-to-one correspondence with the real numbers, with any point corresponding to 0 and any other point corresponding to 1. Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Point-Line-Plane Postulate: Unique Line Assumption Click here to study/print these flashcards.Ĭreate your own flash cards! Sign up here.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
